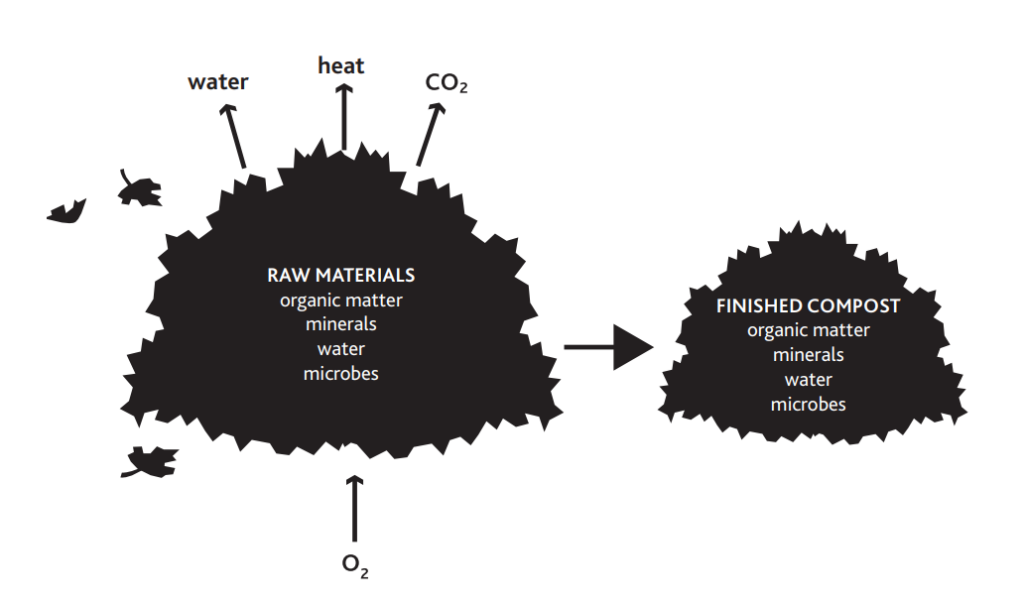
Materials required
- Composting container *
- Shovels
- Nylon
* Major container types
- Open Bin - Low maintenance structure, which could be made from anything from chicken wire to simply piling materials on the ground without an enclosure. The major advantage is the easy access to the Composting material. The disadvantage is that it could be easily accessed by animals, hence yard waste is recommended.
- Closed Bin - Enclosed structure that keeps the Compost together and helps retain moisture and heat. The closed bins usually have an open bottom, which allows for the nutrients from the Compost to travel directly to the soil. The closed bin could be bought or built from accessible materials such as wine crates, plastic storage bins, old wooden dresser drawers, garbage cans, wood palettes or wire mesh. Suitable for Composting food-related waste, as it prevents rodents from entering the bin.
- Tumbler Bin - The tumbler bin is a sealed container, which when aerated well could provide the perfect condition for the Composting process to take place. This container type is recommended when the executor wants to speed up the process of Composting. The tumbler bin could be purchased from gardening stores or made in home conditions.
Steps of Implementation
1. Waste assessment: Determine whether the organic waste available is suitable for Composting. Prerequisites are that the waste is from a compostable material (see Table 1. and Table. 2) and that mixing materials (for the C: N ratio) are available (see “Compost mix structure”). **
2. Site assessment: Determine whether the site structure and the existing infrastructure allow for the establishment of a Composting site. Important considerations here are 1) how much waste is available for the Composting, 2) where will the Compost be placed, 3) is there an availability of a sheltered place (out of direct sunlight and rain) and 4) how would the Compost be accessed in terms of vehicles, trolleys, walking (in the case of the necessity for transportation).
3. Compost container building/provision: Before the Compost mix is created, the storage container should already be available. For more information on the container bins, see “Material requirements”. Furthermore, the Compost container should ensure that the bin has a good drainage system and access to beneficial microorganisms. You can ensure that by placing the container in a spot that is open to bare earth. Don’t position your bin on a concrete floor, as this restricts the access of the Compost to soil microorganisms, which are crucial for decomposition.
4. Compost mix preparation: The chosen materials for Composting should be chopped down into pieces with a particle size not exceeding 2.5cm in diameter. Then all the piled materials should be put into the container bin, by layering the different feedstocks. The following considerations could be taken into account:
- Layer 0: The underneath soil could be considered as the base layer of the Compost
- Coarse/twigs layer: Before applying the organic material in the bin, lay a layer of coarse to provide drainage at the bottom of the container
- Green materials layer: Add 7-10 cm of green materials (such as grass clippings, vegetable waste, etc)
- Soil layer (or finished Compost): Add 2.5-5 cm of soil or finished Compost rich in microorganisms, which could start feeding on the greens.
- Brown materials layer: Add 15-20 cm of brown materials (such as dead leaves, wood chips, shredded newspaper, etc).
- Water layer: Add/sprinkle a layer of water over the dry brown materials. The amount of water depends on the general moisture content of the pile, so check before applying (see “Organic waste characteristics”).
- Repeat from “Coarse/twigs layer” to “Water layer” until the container is full.
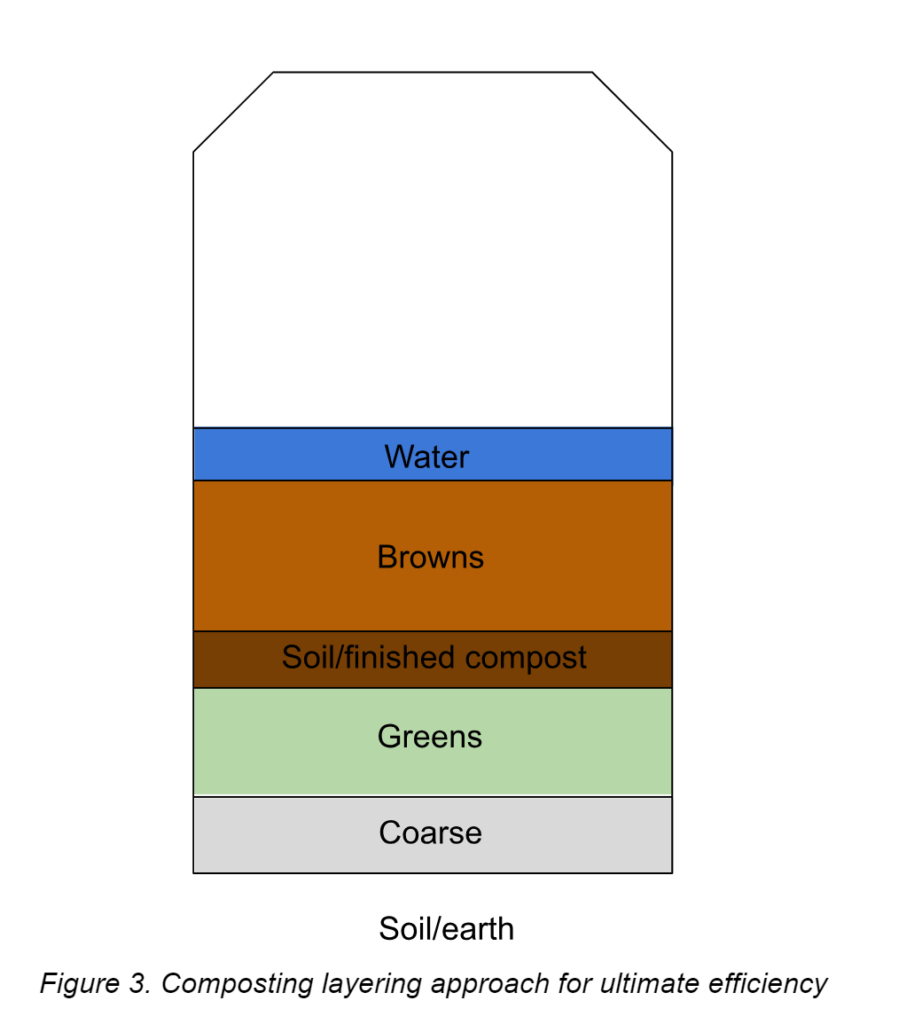
Figure 3. Composting layering approach for ultimate efficiency
5. Composting process: The process of Composting is a microbial-driven process, which happens naturally. Hence, during this process, you want to create the conditions for the process to take place (see more in “Organic waste characteristics”). Furthermore, the process of Composting goes through 4 major stages, where the Compost hummus transforms from organic waste to active decomposed material and finally to cured decomposed material. During these stages, major temperature changes. For a better overview of the stages see Figure 4.
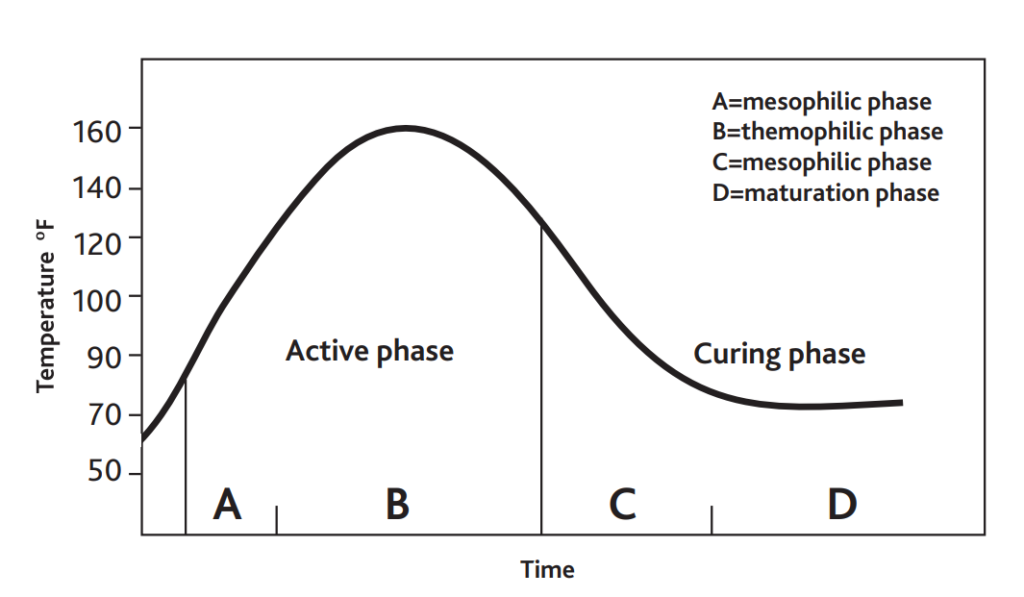
Figure 4. The four stages of the decomposition process and the related temperature changes; (Source: Source)
6. Mixing: Periodically the Compost pile needs to be stirred for the organisms to reach all particles proportionately. Mixing can happen from 1 week to 1/3 weeks.
7. Maintenance: Carry out regular maintenance checks of the Compost material and the container bin. Maintenance checks should be conducted every week. The maintenance checks should consider:
- Check for undesirable odours emitted from the Compost. If those are present then either the oxygen content is low or the water content is imbalanced.
- Check the moisture content by using the “squeeze approach” and remove or add water if necessary.
- Check the temperature of the Compost to see at which stage the Compost is at.
- Check for any defects in the container structure and if those are present - repair/replace the container if necessary.
- If additional Composting feedstock is available then add to the Compost pile, but consider that that can slow the time of application.
The Composting process could take any amount of time between 2-6 months depending on the feedstock materials and the conditions under which the Compost is maturing. A way to recognise the final composed material is when the Compost stops emitting heat. The final Compost should smell earthy, should be comparatively homogeneous and not contain big chunks of materials. Finally, the final Compost should have a dark brown color, similar to regular soil.
8. Application: Compost applications vary per land type, weather conditions and region (source). For agricultural applications Compost is best applied before sowing or planting. In the case of seasonal climatic extremes (such as drought, rainy time, and frost), then Compost should be avoided.
** Compost mix structure
- Compost building blocks → Important consideration is that during the process of decomposition, two elements are crucial and those are carbon (C) and nitrogen (N). C provides the energy source and building block of microbial cells, while N is a crucial component of the proteins and other cells necessary for cell growth and function (source).
- Feedstock C and N content → Some feedstocks are richer in their C and some in their N content (For feedstocks’ prevalence of C and N content see Table. 1). For the Composting process to take place the ideal C: N ratio is considered to be around 30:1 (C: N).
- Organic waste characteristics
-
- Oxygen content/Aeration → For the Composting process to take place, the Compost pile should have access to oxygen (air). Some unwanted side effects of the lack of proper oxidization are undesirable odours, which identify the lack of sufficient oxygen supply. The atmospheric air supply is sufficient for the oxidation process, but with closed and tumbler bins this needs to be regulated more.
- Water/Moisture content → As a rule of thumb the Compost should have a moisture content of 50-60%. A simple approach to check that is the “squeeze approach”. Use a glove, take a handful of the Compost mixture and squeeze. If more than a few drops of water come out, then the Compost mix is too wet. If no water comes out then moisture will need to be incorporated, which could be done by adding up some water.
- Temperature → Temperature within the Compost pile is affecting microbial activities and the rate of decomposition. The ultimate temperature for decomposing is between 40-70˚C (within the Compost pile) and this could be measured with an all-purpose thermometer.
- Feedstock particle size → For the Composting process to take place, the feedstock particle size shouldn’t exceed 2.5cm in diameter. Hence, this means that the feedstock needs to be shredded in advance.
*** Organic waste feedstock that could be used for Composting:
In reality and if the on-land composition allows it, several raw materials could be mixed. A mixture of feedstocks is preferable, as it creates a better range of conditions for the Composting process to take place (Chen et al., 2011). The mixture of several materials could potentially speed up the Composting process and compensate for low moisture content and other biological properties in one or more of the feedstocks.
Warning: Some feedstock types such as animal manure may contain pathogens, which could make the final Compost dangerous and necessitate the use of extra measures. For a full list of dangerous substances click here.
Table 1. Feedstock sources that could be used in Composting
| Feedstock |
Decomposition rate |
Plausible mix combinations |
Carbon (C) & Nitrogen (N) prevalence |
| Hay |
Slow |
Grass clippings, Food scraps |
C |
| Corn stalks |
Moderate |
Grass clippings, Food scraps |
C |
| Straw |
Slow |
Vegetable waste (Not recommended to Compost straw solely) |
C |
| Corn silage |
- |
- |
- |
| Fall leaves |
Slow |
Grass clippings, Vegetable waste |
C |
| Sawdust (Avoid sawdust treated with toxic and chemically treated materials such as plywood) |
Moderate |
Grass clippings |
C |
| Brush, wood chips |
Slow |
Grass clippings |
C |
| Newspaper, Cardboard, Mixed Paper, Paper mill |
Slow |
Green clippings, Vegetable waste |
C |
| Cull potatoes |
Moderate |
Fall leaves, Wood chips |
N |
| Vegetable wastes |
Fast |
Fall leaves |
N |
| Coffee grounds |
Fast |
Fall leaves, wood chips, newspaper |
N |
| Grass clippings |
Fast |
Fall leaves, newspaper |
N |
Considerations for application
- Composting could be a time-consuming process, so consider this before engaging in the process.
- There are some disadvantages to Composting, such as unwanted odours, but also more serious such as an increase in greenhouse gas emissions during the maturation period. For information on plausible disadvantages see link.
This intervention contributes to:



Estimating the cost of Composting depends on a range of factors such as location, scale, amount of waste, waste characteristics, Composting technique used and final use. Hence, the prices outlined below take an average value which considers a range based on different case studies. Furthermore, the costs do not consider a variation in the various approaches of Composting and the costs are average for all these approaches and extra costs could be accrued when applying the different methods. Finally, no depreciation has been applied to the costs, and only present-value prices are considered. Furthermore, costs can fluctuate depending on the inputs used and the type of Composting (e.g. worms in Vermicomposting).
Consider that most capital goods are not disposable and could be used plenty of times. This consideration is crucial as this could significantly decrease the overall costs of the initiative.
Table 1. Costs involved in the building, implementation and maintenance of 1 Composting venue; All prices are taken in 2024 currency value and the main currency is US $
|
Bokashi Composting
(Yield: 3.9 kg ~ 1 gallon)) |
Sheet mulching
(Coverage: 24m2) |
Container Composting
(Yield: 3.9 kg ~ 1 gallon) |
| Major cost contributors |
Bokashi bin
Bin for Bokashi teas storage
~ 19 kg of food waste
1 kg bokashi bran |
Mulch/compost
Newspapers & cardboards |
Kitchen compost bin
Gloves
Shovel
Wheelbarrow |
| Labour time* |
2-3 h |
5-8 h |
8-24 h (depending on whether the bin needs to be constructed) |
| Maintenance demand |
Weekly |
Weekly |
Weekly |
| Decomposition
period ** |
2-3 weeks |
2-4 months |
~ 4 months |
| Estimated costs |
100-150 US $ |
Free (if mulch and newspapers don’t have to be purchased
200-250 US $ (if mulch and newspapers need to be purchased) |
Free (if all materials are already present to the user)
110 US $ (if all materials for the compost bin and maintenance need to be purchased) |
| Source |
Treehugger |
Lawn Love |
Lomi |
* Labor time includes the amount of time necessary to build up the Composting pile as well as any infrastructure needed for the compost to take place
** The decomposition period is greatly dependent on the materials used and the compost mix properties
Container Composting in the UK
Container Composting involves the use of a container/bin and is also known as “cold” Composting. Some recommended Compost materials are fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, twigs, newspaper, grass clippings, tea bags and eggshells. The project of Huw Richards in the UK offers an easy guide which shows you how to get started with your first-ever Compost bin. Please click here for a step-by-step container Compost guide. Furthermore, this guide provides information on how to make a DIY Compost bin from pallets. Finally, for more information on how to make a long-lasting Compost bin from cedar with a roof, please click here.
Ecuador Composting method in Peru and Ecuador
The Ecuador Composting method is a common Composting practice in Peru and Ecuador. The method uses tree trunks and banana stalks as the basis for the Compost material, over which the organic matter is being piled up. This project, designed by and for small farmers in organic banana farming cooperatives in Ecuador and Peru, focuses on creating community-scale Composting facilities. These facilities improve farmers' livelihoods by eliminating the need for expensive commercial inputs and empowering them with technical skills and knowledge of soil nutrition. This results in enhanced soil biodiversity, higher production yields, and better-quality fruit. Chemical-dependent, monoculture banana production harms biodiversity and increases disease vulnerability. The rising cost of living and expensive organic inputs necessitate sustainable solutions for small family farmers. By establishing their Composting facilities, farmers can produce organic inputs, saving costs and potentially generating additional income if there is a surplus. The project will benefit 178 farming families (426 farmers) by providing them with the skills to create their organic inputs, thus protecting biodiversity and supporting rural livelihoods. The project's outcomes will be shared with over 10,000 members of the International Alliance for Small Family Farming in the Caribbean and Philippines, promoting the replication of this initiative.
Hugelkultur Compost in Dayton, the US
Hügelkultur (from German) is a Composting technique where a mound is constructed from decaying wood debris and any other compostable biomass plant materials. The technique creates a raised bed and it helps improve soil fertility and water retention around and near the mounds. The recommended Compost materials are piling logs, branches and plant waste. The project in Dayton, the US facilitates the nearly a kilometre of Hügelkultur beds, creating a gardening system which does not need irrigation. For a general introduction to how to make a Hügelkultur Compost, please click here. Furthermore, this source provides a comprehensive guide on what to include in Hügelkultur Compost. Finally, for a step-by-step guide on how to build a Hügelkultur garden bed, please click here.
Large scale Bokashi Composting in the Netherlands
Bokashi is a Composting method that converts organic matter into soil amendments, which are used to improve soil nutrient supply and texture. What differentiates Bokashi from the other Composting techniques is the use of specialized bacteria which enable the fermentation of the organic matter. As a result, the fermented material is fed directly into the soil and no maturation time is needed. Recommended Compost materials for Bokashi Composting are food waste, rice, molasses and sugar. The project in the Netherlands presents a large-scale application of the Bokashi Composting at a 1 hectare CSA garden and offers education opportunities for learning how to do Composting. For more information on the basics of Bokashi Composting, please click here. Finally, for a step-by-step guide to Bokashi implementation, maintenance and application, please click here and here.
Trench Composting with wood chips in Texas, the US
Trench Composting includes the digging of a trench/hole, where the organic matter is being placed and covered with soil. The difference from other Composting methods is that the decomposition process happens underground, which makes it slower than those involving more air. The major advantages of trench Composting are that it doesn’t require a lot of equipment to be implemented and it is a viable Composting technique for most places (as it keeps the Compost out of sight). In the case of Millberg Farm in Texas trench Composting is being done using wood chips to maintain the fertility of the dryland vegetable and fruit farm. For step-by-step implementation instructions and plenty of additional information on advantages and disadvantages, please click here.
Vermiculture Composting and worm farming in Butuan, Philippines
Vermicomposting is a type of Composting, which uses worms and other earthworms to decompose the organic matter. The typical use of Vermicompost (the product of Vermicomposting) is as a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer and soil conditioner, due to its water-soluble nutrient content. Vermicomposting can be applied on small-scale and large-scale levels, and it facilitates a variety of organic waste. In the green project in Butuan, a natural fertilizer is being made with the use of worms, which is a win-win solution for both plants and local communities. For a step-by-step guide into Vermicomposting, please click here. Furthermore, for an extensive guide into Vermicomposting, please click here. Finally, if you are interested in vermiculture in general, please click here.