The following are general guidelines which should be adapted to the contextual conditions and the available resources already exist in your area, without the need to buy external materials.
Materials required
Steps of implementation
1. Location/Design: Before establishing a kitchen garden, it is important to carefully select where to place the plots of soil or “garden beds”. Study the area around your house as the placement and orientation should be strategically chosen to control exposure to strong winds, sunlight, rain, water resources and other important factors which may affect the success of the kitchen garden.
Since Kitchen Gardens require irrigation, it can be useful to combine this intervention with rainwater harvesting techniques or the reuse of domestic wastewater, especially in dry areas. These include: rooftop rainwater catchments, harvesting ponds, jumbo jars, ring tanks and many more, click here to read more about water harvesting methods. There are also ways to optimise irrigation such as drip irrigation. It is common practice to put fences or hedges around the garden to prevent wild animals or livestock from entering it. Access to water is equally important, as vegetable gardens will require watering, at least in the initial phase.
2. Soil preparation: When creating the beds, leave space for a footpath between them to make each area accessible. Following this step, prepare the soil, making sure that it is soft, not compacted and free of weeds and big rocks.
To improve the ability of soil to retain water and to stimulate crop growth, it is also important to incorporate some organic matter. There are different ways of doing this, one of which is the “garden layering” method (also called “lasagna garden”) which consists of alternating layers of nitrogen-rich (fresh) and carbon-rich (dry) biomass within the soil. Another way to increase soil organic matter is to integrate kitchen vegetables or crop residues and compost over the years (click here for a detailed explanation about compost). A good practice is to use the unused parts of the vegetables and the vegetable plants, cut them into small pieces and bury them in the soil to preserve the most amount of nutrients possible in the soil and to increase organic matter.
3. Seeding: The seeds are then placed and gently covered in the soil and carefully watered. You can plant different combinations of species and it is good practice to always plant some nitrogen-fixing species - such as beans and other legumes - as they will partially restore the nutrients in the soil. With some experience, you will learn which combination of species grows well near each other. However, it is always important to rotate the vegetables’ position over the years as this will result in better soil quality and a better yield in the long term. If the circumstances allow, it is good to select one or two plants that give the best vegetables and keep their seeds to be able to plant them the following year.
4. Mulching and cover crops: For good soil conservation and water retention, it is important to always keep the soil covered. This can be achieved by mulching (see the Mulching intervention), being careful to leave the space for the seedlings to sprout. To prevent leaving the soil bare and exposed, it is good practice to plant cover crops: fast-growing plants that are planted to cover and enrich the soil, preventing soil erosion, and not to be harvested. Cover crops usually include species such as cowpeas, rye, vetch, mustard, clover, or other species that can be used as fodder or mulch material once the vegetable planting season starts again.
5. Adaptations to climatic conditions
- In dry areas: Water can be a limiting resource which can be a problem even when rainfall catchment techniques are applied. In these cases, several actions can be taken to further optimise soil moisture such as using Swales or planting adaptable trees that will provide shade to the kitchen garden, as a way of minimising water loss from soil. More can be found here.
- In very wet areas or areas with very poor or hard soils: Consider building “raised beds” to drain the excess water which tends to accumulate in the soil.
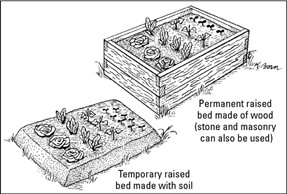
Example of raised beds (source)
6. Maintenance: The amount and cost of maintaining Kitchen Gardens will depend largely on the type of gardening being done, as well as the type of produce being grown. Basic maintenance of the garden is necessary: frequent watering (around 3 times per week), soil quality maintenance (e.g. sufficient fertilization), pest control, etc.
Considerations for Implementation
- Oftentimes, it is important to consider the fencing of a Kitchen Garden. Theft or grazing/destruction by animals is something to take into account.
- Kitchen Gardens may be prone to pests. Nevertheless, it is important to consider the harmful effects of (overusing) chemical inputs such as pesticides and fertilizers on the soil in the long run.
- When installing Kitchen Gardens, care must be taken with the soil, water and fertiliser to revive and maintain the soil quality and ensure crops are well cared for.
Estimation of costs of intervention:
| Description |
Costs |
| Establishment costs (Morocco) |
Between MAD. 2000 - 5000 (US $180 - $450) |
| Labour costs |
US $3.63/day |
| Labour time |
1.5 hours/day in the Kitchen Garden (30 hours per month on garden activities = US $13.02/month) |
| Benefits (Pakistan) |
On average, 28 kg of product was sold in one month, 28 kg product/month/household. Average income US $13.39/month/household. |
| Savings (Pakistan) |
US $9.56/month/household saved because of the availability of vegetables. |
Estimation of costs based on case studies on Sindh Province, Pakistan and the Ounila Valley in the Atlas Mountains of Morocco (source).
Kitchen Gardens and female empowerment, Pakistan
This technique is often practised by women and elderly people as they tend to be the closest to the household. Women and Children/Infant Improved Nutrition in Sindh (WINS) is a four-year project, funded by the European Union (EU), with the overall objective of improving the nutrition status of children, pregnant and lactating women in three districts of the Sindh Province, Pakistan. The Kitchen Gardens intervention is one of the nutrition-sensitive activities of the WINS project, intended to increase year-round access to nutritious foods, thereby bringing down the cost of a nutritious diet and increasing self-sufficiency and improving dietary diversity.
Kitchen Gardens as a key to nutritional well-being, Laos
In a project focusing on improving nutrition in rural areas of Laos, home gardens played a central role. These gardens were set up in households to provide fresh produce for families. Initially, many children in these communities were underweight or suffering from malnutrition, but after the project started, there was a noticeable improvement. The project involved collaboration between various government departments, like agriculture, health, and education, as well as organizations like the Lao Women’s Union. They provided training and resources to help families set up and maintain their gardens. As a result, families were able to grow a variety of fruits and vegetables, which not only improved their diets but also provided a source of income when surplus produce was sold. The project also promote community gardens, where larger-scale farming could take place, benefiting more households. Overall, the success of the project showed that home gardens can significantly improve nutrition and livelihoods in rural areas. It's recommended to expand similar initiatives to other regions and continue supporting them with resources and training.
Kitchen Gardens in the High Mountains, Morocco
In the High Atlas Mountains of Morocco, the Living School in the village of Timmit stands out for its unique curriculum and approach to education. Led by Joana Baumann and Lukas Muller, the school integrates permaculture principles into its teachings, aiming to create a sustainable and inclusive future. The school's surroundings feature a range of sustainability initiatives, including Kitchen Gardens, compost toilets, chicken coops, rain harvesting systems, and reforestation efforts. These initiatives reflect the school's commitment to hands-on learning and environmental stewardship. Permaculture, a key focus of the school, emphasizes creating natural cycles and fostering self-sustaining ecosystems. Through permaculture principles like Earth care, people care, and fair share, students learn to work with nature to build resilient communities and land. Despite challenges in convincing the local community of the project's value, Baumann and Muller emphasize the importance of creating a demonstration site and allowing community members to witness the benefits firsthand. Their efforts have garnered trust and support from the community, leading to increased interest in alternative forms of education and sustainable practices. Baumann and Muller's dedication to the project exemplifies their commitment to creating positive change and empowering local communities. Through their efforts, they hope to inspire future generations to embrace sustainability and take ownership of their environment.
Community Gardens as food security for local communities, Nepal
In the context of Nepal, the assessment of landscape interventions such as perma gardens and Kitchen Gardens reveals their pivotal role in enhancing household food security and resilience. These interventions effectively mitigate production shocks like crop pests and water shortages, crucial challenges faced by local communities. Permagardens, characterized by higher yields and environmental benefits, offer a sustainable solution to food insecurity. On the other hand, Kitchen Gardens, with their ease of management and teaching, provide accessible pathways for communities to engage in food production. Overall, these landscape interventions not only bolster food security but also foster skills transfer and community empowerment. They serve as compelling examples of how local initiatives can effectively address pressing challenges and build resilience in Nepal's agricultural landscape.
Kitchen Gardens in Douar Anguelz Ounila, Morocco
As a result of overgrazing and tree-cutting, the region of Anguelz in Morocco has been facing severe land-related stresses in the past decade. Where once lay lush and vibrant mountains, now the landscape has turned completely arid. With the help of Perma Atlas the people from Anguelz have come together to regreen the landscape and bring it back to its former healthy state. A major issue that the area is facing is the lack of rain and seasonal flooding events. Together with the local farmer Omar, Perma Atlas constructed the first kitchen garden in the area. Since it’s inauguration the intervention has been thought to the rest of the community, in order to inspire others to make their own. In Morocco Kitchen Gardens are used to cultivate vegetables, herbs and fruits for use in the kitchen and provide sustenance for small households, whilst making use of neglected land. Kitchen Gardens often have space for livestock as well as for trees and hedges to produce fodder. It took 26 days for Omar to construct the kitchen garden with bare hands, by bringing stones and setting up a backfill more than 2 meters high. Surprise crops can be sold at the market to generate additional income helping communities to produce their own food supply. Omar and the Perma Atlas team have engaged with other local farmers to share their knowledge and show other how to implement this technique. According to local citizens, introducing Kitchen Gardens is also a way to bring back agriculture to the region, which has suffered from from the process of urbanization.
